作成したプリファレンスを他のアプリケーションと共有するには:Androidアプリケーション開発者のためのTips集(18)
Androidアプリ開発者のためのTips集。今回は、作成したプリファレンスを他のアプリケーションから使用する方法について解説する。アプリの設定情報の共有などに便利だ。
Tips概要と動作検証環境
| 用途 | 便利 |
|---|---|
| カテゴリ | データI/O |
| レベル | 中級 |
| 動作確認環境 | Android 2.3.3(GingerBread) エミュレータにて動作確認 |
| 備考 | 今回のTipsは上記環境で動作確認・検証を行っています |
Tips18:作成したプリファレンスを他のアプリケーションと共有するには
前回、前々回に引き続き、Androidにおけるデータ保存方法の1つ「プリファレンス」について紹介する。
今回は、作成したプリファレンスを他のアプリケーション(以下、アプリ)から使用する方法について解説する。プリファレンスは、主にアプリの設定情報などの保存に使用されるため、複数のアプリで設定内容を共有したい場合に便利だ。
| 関連リンク: | |
|---|---|
| ⇒ | プリファレンスを使用したデータの保存 |
| ⇒ | プリファレンスを使用した設定画面の作成 |
大まかな手順
プリファレンス作成時のモード設定により、他アプリからでもプリファレンスに保存したデータを参照できる。以下は、その前提条件である。
- プリファレンスを作成して、データを保存するアプリは、他アプリが読み込めるモードでプリファレンスを作成する必要がある
- 他アプリで作成されたプリファレンスを参照するアプリは、対象アプリのContextを使用してプリファレンスを開かなければならない
それでは、具体的な手順を見ていこう。
他アプリからアクセス可能なプリファレンスを作成する
プリファレンスの実体は、“テキストファイルの読み書き”である。他アプリからアクセスできるかどうかは、言ってみれば“ファイルのアクセス権”の問題である。その権限を設定してやればよい。
getSharedPreferences()メソッドでプリファレンスを作成する際、モード「Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE」を指定することにより、他アプリからでもファイルの読み込みが可能になる。
/** 他アプリケーションから読み込み可能なプリファレンスの作成例 */
public SharedPreferences getReadablePreference( Context context, String prefName ){
return context.getSharedPreferences( prefName, Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE );
}
他アプリケーションのプリファレンスへのアクセス
他アプリが作成したプリファレンスにアクセスするには、そのアプリのContextを作成して、プリファレンスを開く必要がある。
他アプリのContextを作成するには、Context#createPackageContext()メソッドを使用する。
Context#createPackageContext ( String packageName, int flags )
第1引数の「packageName」には、対象アプリの“パッケージ名”を指定。第2引数の「flag」には、取りあえず“0”を指定しておけばよい。ただし、対象のアプリが端末にインストールされていない場合は、「NameNotFoundException」が発生するので注意してほしい。
/** 他アプリケーションのContextを作成する例 */
public Context createOtherContext( Context context, String packageName ){
try{
return context.createPackageContext( packageName, 0 );
}catch( NameNotFoundException e ){
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
使用例
今回、例として以下の2つのアプリを作成した。
- ユーザーに「名前」「年齢」「職業」「敬称要否」を入力してもらい、プリファレンスに登録するだけのアプリ
- 上記アプリのプリファレンスから「名前」「年齢」「敬称要否」を読み込んで、ドロイド君がユーザーにあいさつするアプリ
*例1:プリファレンスに登録するアプリ
まずは、プリファレンスに登録する側のアプリを見てみよう。以下は、プリファレンスにデータを保存する部分の実装例である(レイアウトなどのテーマに関係ない部分は割愛している)。
/** 他アプリケーションから読み込み可能なプリファレンスの作成例 */
public SharedPreferences getReadablePreference( Context context, String prefName ){
return context.getSharedPreferences( prefName, Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE );
}
/** ユーザーのプロフィールをプリファレンスに保存する */
public void saveUserProfile( Context context, String name, int age, String job, boolean needTitle ){
// プリファレンスの準備
SharedPreferences pref = getReadablePreference( this, "name_and_age" );
// プリファレンスに書き込むためのEditorオブジェクト取得 //
Editor editor = pref.edit();
// "user_name" というキーで名前を登録
editor.putString( "user_name", name );
// "user_age" というキーで年齢を登録
editor.putInt( "user_age", age );
// "user_job" というキーで職業を登録
editor.putString( "user_job", job );
// "user_title" というキーで敬称要否を登録
editor.putBoolean( "user_title", needTitle );
// 書き込みの確定(実際にファイルに書き込む)
editor.commit();
}
*例2:ドロイド君があいさつするアプリ
次に、ドロイド君があいさつするアプリを見てみよう。こちらも今回のテーマに関連しない部分は割愛し、プリファレンスの読み込み部分の実装例にフォーカスする。
/** 他アプリケーションのContextを作成する */
public Context createOtherContext( Context context, String packageName ){
try{
return context.createPackageContext( packageName, 0 );
}catch( NameNotFoundException e ){
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/** 他アプリケーションのプリファレンスを読み込む */
public SharedPreferences getOtherOnesPreference( Context context, String prefName ){
// プリファレンスを保存したアプリケーションのContextを作る
Context otherOnesContext = createOtherContext( context, "jp.test.preference.share" );
// プリファレンスを「MODE_WORLD_READABLE」で開く
return otherOnesContext.getSharedPreferences( prefName, Context.MODE_WORLD_READABLE );
}
/** プリファレンスから名前を取り出す。登録されていなければ空の文字列を返す */
public String loadName( Context context ){
// プリファレンスの準備
SharedPreferences pref = getOtherOnesPreference( context, "name_and_age" );
// "user_name" というキーで保存されている値を読み込む
return pref.getString( "user_name", "" );
}
/** プリファレンスから年齢を取り出す。登録されていなければ「-1」を返す */
public int loadAge( Context context ){
// プリファレンスの準備
SharedPreferences pref = getOtherOnesPreference( context, "name_and_age" );
// "user_age" というキーで保存されている値を読み込む
return pref.getInt( "user_age", -1 );
}
/** プリファレンスから敬称要否を取り出す。登録されていなければ「true」を返す */
public boolean loadNeedTitle( Context context ){
// プリファレンスの準備
SharedPreferences pref = getOtherOnesPreference( context, "name_and_age" );
// "user_age" というキーで保存されている値を読み込む
return pref.getBoolean( "user_title", true );
}
実行結果
実行結果は、以下の通りだ(画像1、2)。
≫連載「Androidアプリケーション開発者のためのTips集」の目次
関連記事
Copyright © ITmedia, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
組み込み開発の記事ランキング
- パナソニックの弱いロボット「NICOBO」がLLMでさらなる進化、累計販売は1万体に
- ソニーがSTB不要のデジタルサイネージを提案、AIデジタルヒューマンも組み込める
- Rapidusの顧客獲得が進捗、60社以上と協議中で約10社にPDKをライセンスへ
- あなたの家電がサイバー攻撃の踏み台に? 購入時は星マークをチェックしよう
- 家電のノジマがロボットショールームにヒューマノイドや業務用を展示する理由
- 製造業の「SBOM」は誰が構築し運用/管理すべきか【後編】
- スバルが制御統合ECU向けマイコンにインフィニオンの「AURIX TC4x」を採用
- チップレットでASIL Dを支援する車載SoC技術を開発
- 出荷量1.3倍を実現、電源不要のIoTゲートウェイが南種子町にもたらす農業改革
- 一度の顔登録で複数サービス利用可能 NECの顔認証基盤、トライアルなどで実証導入へ
コーナーリンク

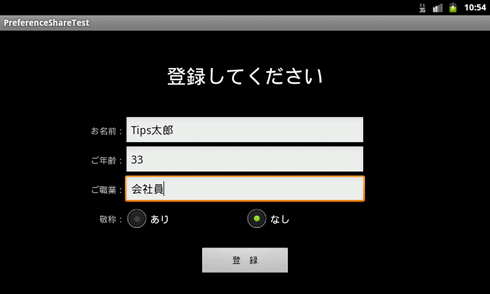 画像1 アプリ1:登録用アプリで名前などを登録
画像1 アプリ1:登録用アプリで名前などを登録 画像2 アプリ2:別のアプリから登録内容を読み込んで使用
画像2 アプリ2:別のアプリから登録内容を読み込んで使用


